In this post:
Iron Definition | Iron-Deficiency Anemia | Do I Need to Eat Meat? | Foods that Increase Iron Absorption | Foods that Decrease Iron Absorption | 16 Plant-Based Iron Sources + Recipes | Sample Day of Eating
Hi Sweet Friends,
I’m often asked if I get enough iron through my plant-based diet. The short answer is heck yeah! But the longer answer breaks down why iron is important, where to get it, and what to do if you’re deficient and that’s a bit more complex.
That’s why I teamed up with Crazy Sexy RD, Jen Reilly for this blog post. We’ve broken things down so that plant-powered readers can feel confident about meeting their iron needs.
Key Takeaways ✔
First, Let’s Cover the Basics: What Is Iron?
So glad you asked! Iron is an essential mineral whose main job is to produce hemoglobin to carry oxygen from our lungs to the rest of our body. Iron is also key in the creation of myoglobin in muscle cells (which also transports good ole’ O2 to cells). Iron is even important for energy metabolism. It’s also part of the enzymes that are essential for tip-top digestion and overall body health.
The health benefits of iron make it an important ingredient in healthy eating. Without enough iron, red blood cells are fewer and smaller, which means they’re not transporting sufficient oxygen where it needs to go. When this happens, your organs and tissues can’t work as well as they should (keep reading for more on that!).
Iron Deficiency Anemia: What Happens When You Have an Iron Deficiency
Iron deficiency anemia—sometimes spelled as iron deficiency anaemia—is actually the most common nutritional deficiency in the US.
Iron deficiency anemia develops when you don’t have enough iron in your body (source), sometimes from a lack of iron-rich foods in one’s diet.
An iron deficiency can lead to delayed motor and mental functioning in infants, small or pre-term babies for pregnant women, fatigue, lightheadedness, headaches, grumpiness, inability to concentrate, and impaired mental clarity in adults and teens (source).
If you suspect that you may be iron deficient, make an appointment with your doc. He or she will probably look for signs of anemia such as pale skin, irregular heartbeat, and rapid breathing, and do an exam to check for internal bleeding. But, most commonly, iron deficiency is found by doing a blood test that tests for hemoglobin and hematocrit levels.
What if you’re eating iron-rich foods and you’re still anemic?
Should You Take an Iron Supplement?
It’s possible to eat lots of iron-rich foods (plant-based or not) and still be anemic. This may be because of a weakened digestive system due to celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease, or other conditions that cause insufficient stomach acid.
In these cases, iron supplements may be warranted. A daily dose of 25-50 mg of iron may be helpful (swig that supplement down with some vitamin C-rich green juice!) until iron levels hit the recommended range. But always, always check with your doc for specific recommendations.
It’s about finding a delicate balance. Excess iron can damage your liver, heart, and pancreas. So you do want to make sure you’re not taking too much iron.
Need help finding balance? Let me give you a kickstart!
Do You Need to Eat Meat to Increase Your Iron Intake?
Nope! There are plenty of iron-rich vegetarian foods. But I like to give you guys the full scoop, so let’s clarify a few things. There are two kinds of iron:
- Heme Iron: Heme is found in red meat, fish, and poultry. This type of iron is in foods that contain hemoglobin. The body absorbs 7-35 % of heme iron (more readily absorbed than non-heme iron).
- Non-heme Iron: Non-heme iron is found in numerous plants. The body absorbs 2-20% of non-heme iron. The percentage is lower because this type of iron is more sensitive to other dietary factors that may limit its absorption (more on how to avoid that in the next section).
It’s worth mentioning that while meat protein nearly doubles the absorption of non-heme iron, vitamin C is also effective to help your body absorb iron and doesn’t have the associated risk of increased heart disease like the iron only found in meat.
The good news is that iron needs can be met completely with iron from plant sources. It’s just important to pay attention to the factors that may affect absorption—especially if someone is iron deficient. And, it means you’ll have to eat more vitamin c rich foods.
Plant Foods that Increase Iron Absorption
Drumroll please…You can enhance iron absorption by eating foods—you got it—rich in vitamin C.
Vitamin C Rich Foods
No need for iron supplementation! You can improve iron absorption by eating foods high in vitamin C. Combine iron-rich foods in the same meal with these vitamin C-rich foods to improve your body’s ability to absorb iron more efficiently:
- Papaya
- Bell peppers
- Broccoli
- Brussels sprouts
- Kiwi
- Pineapple
- Citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruit, strawberries)
- Cauliflower
Vitamin C is an acid (ascorbic to be exact), and acids increase the bioavailability of iron. Bottom line: Increase iron absorption and add these foods to your plate with foods high in iron every day!
Foods that Inhibit Iron Absorption
Absorption of plant-based iron can be decreased when certain foods are part of the meal. But, keep in mind that unless you’re genuinely iron deficient and need to maximize iron absorption at every turn, these foods and supplements in your diet shouldn’t make a big impact on your iron status.
Tannins
Tannins found in herbal teas, peppermint tea, red grapes, chocolate, and coffee reduce iron absorption (study here). So you should avoid drinking coffee, red wine, tea etc. while eating foods high in iron. However, consuming these foods an hour before or an hour after the iron-rich meal does not affect iron absorption.
Phytates
Phytates are important antioxidants and anti-inflammatory plant compounds found in the highest quantities in whole grains, wheat bran, soybeans, pinto beans, kidney beans, and peanuts. Oddly enough, some of the foods that are high in iron also contain high amounts of phytates.
Phytates bind to plant-based iron and lower its absorption. But soaking, fermenting, sprouting, and cooking all reduce phytate content by 50-75%. So, the chance of phytates truly affecting iron absorption is pretty slim, especially since most plant foods contain some iron and only a few raw plant-based foods contain notable levels of phytates.
Here are some foods that impact iron absorption:
- Egg Protein (both the yolk and the white)
- Calcium Supplements and Dairy Foods compete with iron for uptake in your intestinal tract
- Zinc and Manganese supplements
- Peppermint and Chamomile
- Antacids decrease iron absorption because they reduce stomach acid
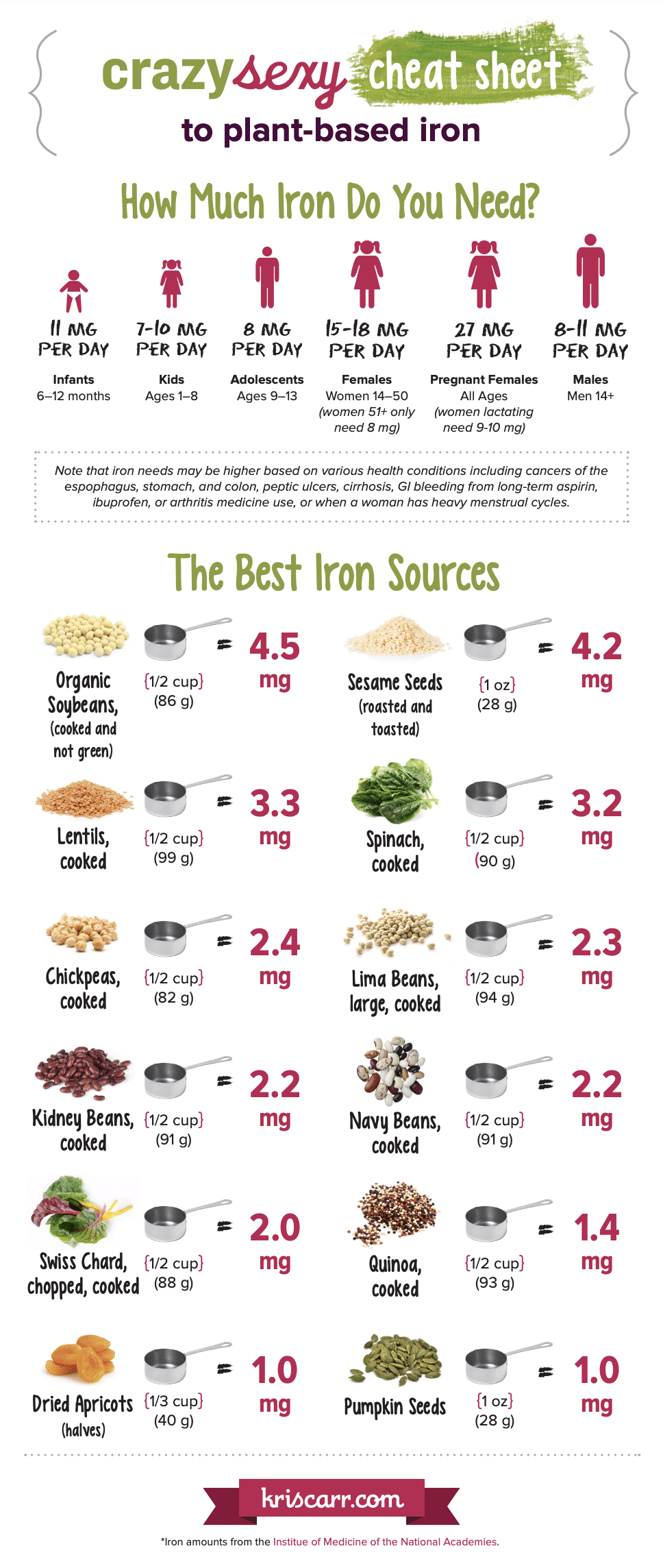
16 Plant-Based Iron Sources
Many plant-based foods are iron rich and can provide an adequate iron intake. There are the top 16 plant-based foods you can use to give your diet the iron boost that it needs (and we threw in some delicious iron-rich recipes, too).
1. Organic Soybeans
Soybeans pack a powerful punch and should be a staple in any vegetarian or vegan diet. Soybeans contain 4.5 mg of iron per serving (1/2 cup or 86 grams).
2. Sesame Seeds
Roasted and toasted sesame seeds contain 4.2 mg of iron in a 1 oz. (28 g) serving. You can eat your sesame seeds in yummy bars like this one, sprinkle some on top of this Broccoli Curry Udon, or make Turmeric Herb Falafel or Raw Carrot Falafel.
3. Lentils
Eating a half cup (99 g) of cooked lentils will get you a serving of 3.3 mg of iron. On busy days, I love making simple soups like this 1-Pot Lentil, Potato and Spinach Soup or this Sweet Potato & Lentil Soup.
4. Spinach
These dark green leafy vegetables contain 3.2 mg of iron per 1/2 a cup serving (90g). Beet greens pack a similar nutrient punch. You can’t go wrong with ripping and dipping your favorite pita bread in a bowl of vegan Spinach Artichoke Dip!
5. Chickpeas
Cooked chickpeas (also called garbanzo beans) contain 3.3mg of iron per a 1/2 cup (82g) serving. My favorite way to eat chickpeas is in a yummy hummus! Here’s a few scrumptious hummus recipes:
- Smoky Southwestern Hummus
- Basil Hummus Stuffed Mushrooms
- Sweet Potato Hummus
- Hummus Tartine with an Olive, Tomato, Lemon and Basil Salsa
6. Lima Beans
These lil’ lima beans contain 2.3 mg of iron 1/2 a cup (94 g) when cooked.
7. Kidney Beans
I’m not kidding when I tell you that a 1/2 cup serving of cooked kidney beans contains 2.2 mg of iron per serving. They’re great in soups, chili, and bean salads! Another fantastic recipe you should try if you want to eat more kidney beans is this one for Chili Quinoa Bean Bites With Chipotle Mashed Sweet Potatoes.
8. Navy Beans
These great beans are next, and also contain 2.2 mg of iron per 1/2 cup serving (91 g).
9. Swiss Chards
Cooked swiss chard contains 2 mg of iron per cup 1/2 cup serving. This Butternut Squash and Chard Vegan Lasagna is a great one to feed the whole family!
10. Quinoa
Quinoa is an ancient grain that contains 1.4 mg of iron per 1/2 cup serving. Try one of these iron rich meals:
11. Dried Apricots
Finally, a fruit! Dried fruits like apricots can be good sources of iron. Dried apricots contain 1 mg of iron per 1/3 cup serving (or 40 g).
12. Prune Juice
This one might surprise you, but prune juice contains 2.9 mg of iron per cup! Prune juice is also well-known for helping you poop!
13. Pumpkin Seeds
Pumpkin seeds are another great source to help you get more iron in your diet, containing 1 mg of iron per 1 oz. serving. These are a yummy snack on their own when baked with a little oil and salt or great addition to a salad for some added crunch. You can even use them in vegan mac & cheese. Hemp seeds and sunflower seeds are other great seeds to eat.
14. Dark Chocolate
Dark chocolate is a special treat that contains 7 mg of iron in a 3 oz serving. Win-win!
15. Blackstrap Molasses
You didn’t expect this one, did you? Blackstrap molasses contains around 1.9 mg of iron per two tablespoons (you’ll just want to limit how often you incorporate it into your diet because of the high sugar content).
16. Baked Sweet Potatoes (and Regular Potatoes)
Sweet potatoes contain around 2.2 mg of iron in a single serving (a potato). Baked Potatoes with the skin have around 2 mg of iron. This versatile veggie can be served as a falafel, hummus, soup, added to a quinoa bowl, cut into french fries, turned into a burger, stuffed with other yummy goodness, and so much more!
Honorable mentions include things like fortified breakfast cereal, coconut milk, amaranth, and cannellini beans.
As you can see, many plant foods are rich in iron content and there’s an endless amount of delectable ways to eat them. To help you get started, here’s a sample of what you can eat in a day to increase your iron intake!
Sample Day of Iron for a 40-Year-Old Woman
How much iron does a women of reproductive age need to eat? Most adults need at least 8mg of dietary iron intake per day. Women should shoot for more, specifically 15-18 mg per day. Here’s what it could look like!
- Breakfast: ⅓ cup rolled oats (1.2 mg) cooked with 1.5 oz raisins (1 small box, 0.8 mg iron) = 2 mg iron
- Snack: 8 ounces of green juice (pack in those leafy greens)
- Lunch: Lentil Spinach Soup (1 cup lentils [6.6 mg ] + ½ cup cooked spinach [3.2 mg]) with bell pepper salad = 9.8 mg iron
- Snack: Veggies and rice crackers with tahini dip (made with 1 oz sesame seeds) = 4.2 mg iron
- Dinner: 1 cup sautéed Swiss Chard (2 mg) over 1 cup cooked quinoa (2.8 mg) with lemon = 4.8 mg iron
TOTAL: 20.8 mg of iron
I hope we’ve demonstrated that iron is one of the proteins essential to a vegetarian diet and that there are plenty of plant-based food groups that can provide the iron you need without turning to animal products.
Iron comes up a lot when you’re talking about a plant-based diet, but I know there are a lot of other questions flying around out there. What curiosities pop up in your conversations about eating a plant-empowered diet (even if you’re not 100% vegan)?
Peace & Popeye,



Iron is a mineral that serves several important functions, its main being to carry oxygen throughout your body and making red blood cells
is very good,
Wow! It’s really a good one. To improve your red blood cells this blog gives us the exact information about how to improve iron in a human body. Thanks for sharing such an informative article.
Thank you for all the helpful info. I have always been interested in health but, have slipped into some bad dietary habits, consuming too much sugar, etc. I feel inspired to go with the greens.
Thank you for the excellent article and infographic! We just found out my husband is anemic and we’re eating a plant- based diet.
This blog post is a fantastic resource for vegans and vegetarians with regards to iron! Thank you so much for sharing. I learned some things reading this and am going to actively be aware of what foods I am pairing together to help me absorb the most iron possible.
Who made this incredible photo ?
Hi Kris,
A little over 3 months ago I learned my ferritin levels were very low- an 8 to be exact. I’ve been vegan for nearly two years now, and I eat a whole food plant based diet, including lots of greens, nuts, and legumes. I am also extremely active (fitness and yoga instructor by profession). I couldn’t believe how low my iron stores were, and although I’m resistant to taking an iron supplement, I figured it was necessary in this case. However, after 3 months of taking the supplement, my next blood test showed my ferritin went DOWN! I’m shocked. I can’t understand how this happened, so I’m seeking other opinions outside of my regular doctor. Any advice or suggestions you have?? I definitely don’t want to go back to eating meat, as many are telling me to do. I appreciate any insight!
Thanks!
Do you take anything that inhibits iron absorption within an hour or two before or after taking your iron or eating an iron-rich meal? Ibuprofen, turmeric, coffee, tea, zinc, and more can all inhibit iron absorption.
Also, if you’re deficient in B12, which is only found in animal products, that could play a role, so you should supplement with both. I’ve learned this the hard way after experiencing iron deficiency myself.